What is Image Sensor Size, its importance and application?
Published on: Aug 12, 2024

Written by: Admin
What is Image Sensor Size?
Image sensor size, measured in millimeters, refers to the dimensions of a camera's sensor. Larger sensors capture more light, enhancing image quality, with sizes ranging from full-frame to 1/2.3-inch.
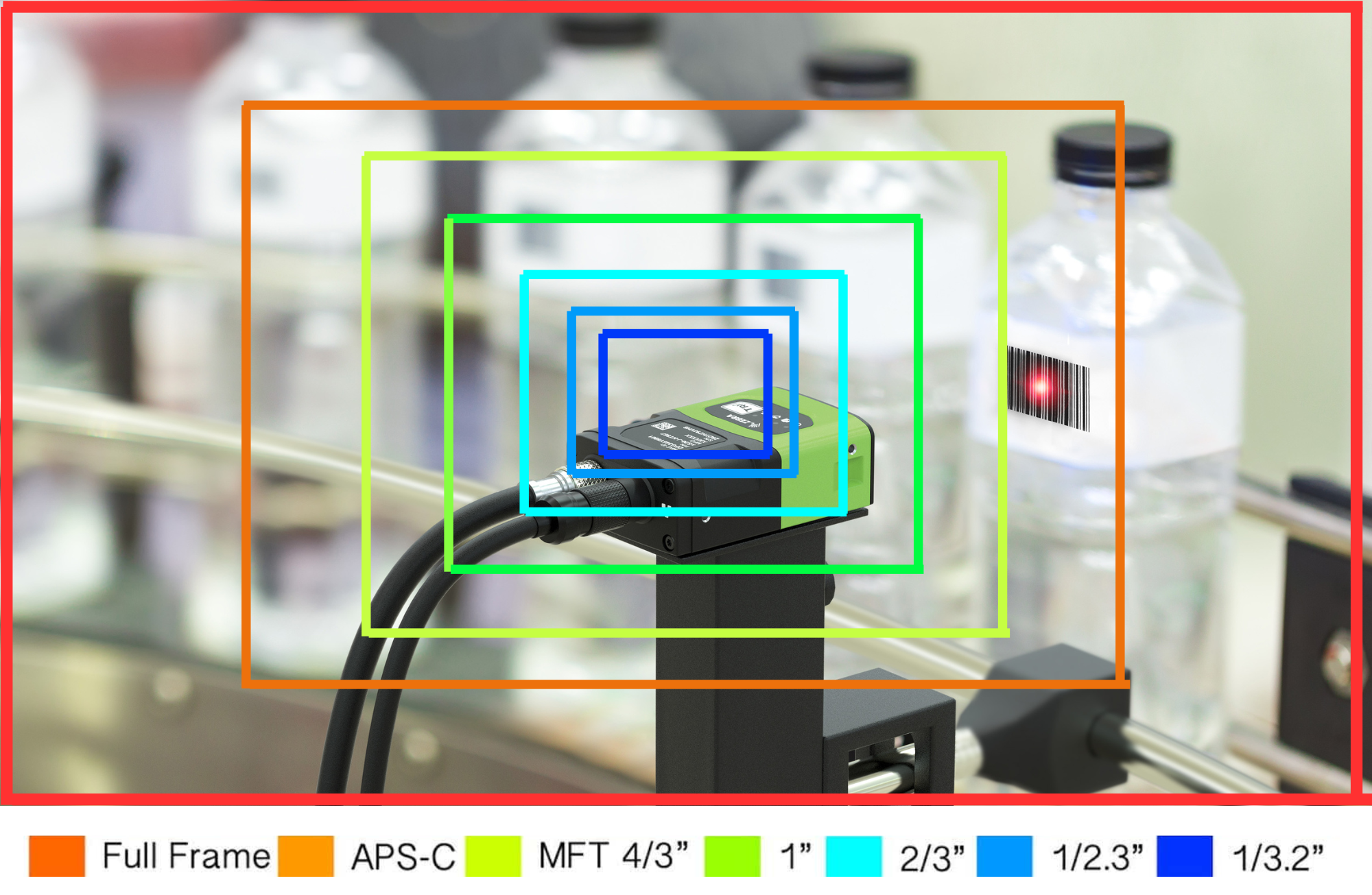
Importance of Image Sensor Size
1. Light Sensitivity and Low-Light Performance
- Larger Sensors: Have larger pixels that can capture more light, resulting in better performance in low-light conditions and less noise.
- Smaller Sensors: Tend to struggle in low-light situations and may produce noisier images.
2. Depth of Field and Bokeh
- Larger Sensors: Provide a shallower depth of field, allowing for more pronounced background blur (bokeh). This is desirable in portrait photography where the subject is sharp but the background is beautifully blurred.
- Smaller Sensors: Have a deeper depth of field, which keeps more of the image in focus. This can be useful for landscape photography where you want both the foreground and background to be sharp.
3. Image Resolution
- Pixel Density: Larger sensors can house more and larger pixels without crowding, which can lead to higher resolution images with finer details.
- Dynamic Range: Larger sensors typically offer a greater dynamic range, capturing more details in both the highlights and shadows of an image.
4. Lens Compatibility and Field of View
- Full-Frame Sensors: Provide a wider field of view with the same lens compared to smaller sensors. This is important for wide-angle photography.
- Crop Factor: Smaller sensors have a crop factor that effectively increases the focal length of the lens. For example, an APS-C sensor typically has a crop factor of 1.5x, meaning a 50mm lens will have an effective focal length of 75mm.
When Do We Need a Bigger Sensor?
1. Professional Photography
- High Image Quality: Professional photographers often need the highest possible image quality, which larger sensors provide. This includes better low-light performance, higher resolution, and superior dynamic range.
- Printing Large Images: For prints that are large or intended for close-up viewing, the higher resolution from larger sensors ensures that the images remain sharp and detailed.
2. Portrait Photography
- Shallow Depth of Field: Larger sensors allow for a shallower depth of field, which helps in achieving a pleasing background blur (bokeh) that is often desired in portrait photography.
3. Low-Light Conditions
- Improved Performance: In environments with limited light, such as indoor events or nighttime scenes, larger sensors perform better by capturing more light and producing less noise.
4. Landscape Photography
- Dynamic Range: Capturing the wide range of tones in a landscape scene, from bright skies to dark shadows, benefits from the higher dynamic range of larger sensors.
- Resolution: Larger sensors with higher resolution are beneficial for capturing intricate details in landscape scenes.
5. Video Production
- Cinematic Look: For high-end video production, larger sensors can provide a more cinematic look with shallow depth of field and better low-light performance.
- 4K/8K Recording: Larger sensors are better suited for high-resolution video recording, offering better detail and dynamic range.
The size of an image sensor plays a crucial role in determining the overall image quality, depth of field, low-light performance, and dynamic range of a camera. While smaller sensors are suitable for compact devices and general-purpose photography, larger sensors are essential for professional photography, low-light situations, portraiture, and high-end video production. Understanding the impact of sensor size helps photographers and videographers choose the right equipment for their specific needs, ensuring they can achieve the desired results in their work.

