What are Global Shutter Camera?
Published on: Aug 12, 2024

Written by: Admin
What is a Global Shutter Camera?
A global shutter camera captures the entire image frame simultaneously, exposing all pixels at once, preventing distortions common in rolling shutter cameras that capture line by line.
How Global Shutter Cameras Work
- Simultaneous Exposure:
- All pixels on the image sensor are exposed to light simultaneously and for the same duration. This simultaneous exposure helps eliminate the distortions that occur in rolling shutter cameras, especially when capturing fast-moving objects.
- Electronic Shutter Mechanism:
- After the exposure period, the electronic shutter closes, and the charge accumulated in each pixel is read out and converted into a digital signal.
Key Features and Advantages
- Distortion-Free Imaging:
- Global shutter cameras eliminate the "rolling shutter effect," which is a distortion that occurs when different parts of an image are exposed at different times. This makes them ideal for capturing fast-moving objects without the "jello effect" or skewing.
- Accurate Motion Capture:
- They provide accurate capture of high-speed motion, ensuring that the image remains clear and undistorted.
- Simplicity in Synchronization:
- The simultaneous exposure simplifies the synchronization with other systems or external events, which is critical in applications requiring precise timing.
Applications of Global Shutter Cameras
Global shutter cameras are best suited for applications where high-speed motion needs to be captured accurately, without any distortion. Here are some common use cases:
- Industrial Automation and Robotics:
- Use Case: Monitoring and controlling fast-moving machinery or robotic arms.
- Advantage: Accurate capture of fast motions ensures precise control and monitoring.
- High-Speed Photography:
- Use Case: Capturing events that happen very quickly, such as sports photography or scientific experiments.
- Advantage: High frame rates with distortion-free imaging.
- Machine Vision:
- Use Case: Inspecting fast-moving products on production lines for defects.
- Advantage: Clear, undistorted images of products moving at high speeds.
- Surveillance and Security:
- Use Case: Monitoring areas with fast-moving subjects, such as traffic intersections.
- Advantage: Accurate capture of vehicles or people in motion for reliable surveillance.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
- Use Case: Creating immersive experiences where precise motion tracking is crucial.
- Advantage: Clear and accurate capture of movement enhances the user experience.
- Scientific Imaging:
- Use Case: Recording high-speed phenomena in research applications
- Advantage: Distortion-free capture of rapid events for accurate analysis.

When to Use Global Shutter Cameras Over Line Shutter Cameras
Global shutter cameras are preferred over line shutter cameras in the following scenarios:
- Fast-Moving Objects:
- When capturing fast-moving subjects where distortion-free imaging is crucial. Line shutter cameras may struggle with motion artifacts in such cases.
- Precision Timing:
- When precise synchronization with external events or systems is required. Global shutters offer simplicity in synchronization due to simultaneous exposure.
- Compact and Integrated Systems:
- In applications where integrating a scanning mechanism for line shutter cameras is impractical or where space is limited.
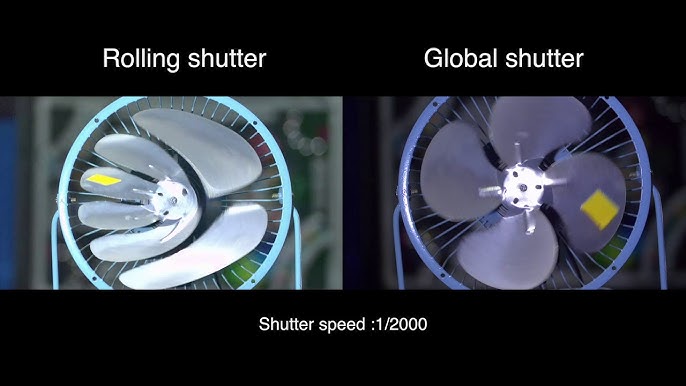
Global shutter cameras offer significant advantages in capturing fast-moving objects without distortion, making them ideal for applications requiring high-speed, accurate, and distortion-free imaging. They are particularly useful in industrial automation, high-speed photography, machine vision, surveillance, AR/VR, and scientific imaging. When choosing between a global shutter camera and a line shutter camera, consider the specific requirements of your application, including the need for motion capture accuracy, synchronization simplicity, and spatial constraints.

