What is Contact Image Sensor CIS camera?
Published on: Oct 08, 2024

Written by: Soumen das
An Introduction to CIS Cameras: Advanced Imaging for Industrial Applications
A Contact Image Sensor (CIS) camera is a high-performance imaging system designed primarily for industrial and scientific applications where precision and speed are critical. CIS cameras offer a unique blend of high resolution, compact design, and superior image quality, making them ideal for a wide range of surface inspection and defect detection tasks. These cameras are often used in industrial automation, quality control, and machine vision systems due to their ability to capture detailed, line-by-line images of objects with remarkable clarity.
In this article, we'll dive into the technical aspects, key features, and common use cases of CIS cameras. Understanding these details will help you grasp why CIS cameras are gaining popularity in industrial and automated environments.
What Is a CIS Camera?
At its core, a CIS camera uses multiple linear sensors that capture images line by line as objects pass by the camera, rather than capturing the entire scene at once like traditional area-scan cameras. CIS technology originated in the document scanning industry, where high-precision, flatbed scanning was needed. Over time, this technology evolved to meet the demands of industrial applications such as surface inspection and high-speed defect detection.
A CIS system consists of a light source, an optical lens system, and a sensor arranged in a compact linear configuration. This design allows the CIS camera to scan objects as they move across its field of view, capturing a high-resolution image of the object’s surface with minimal distortion.
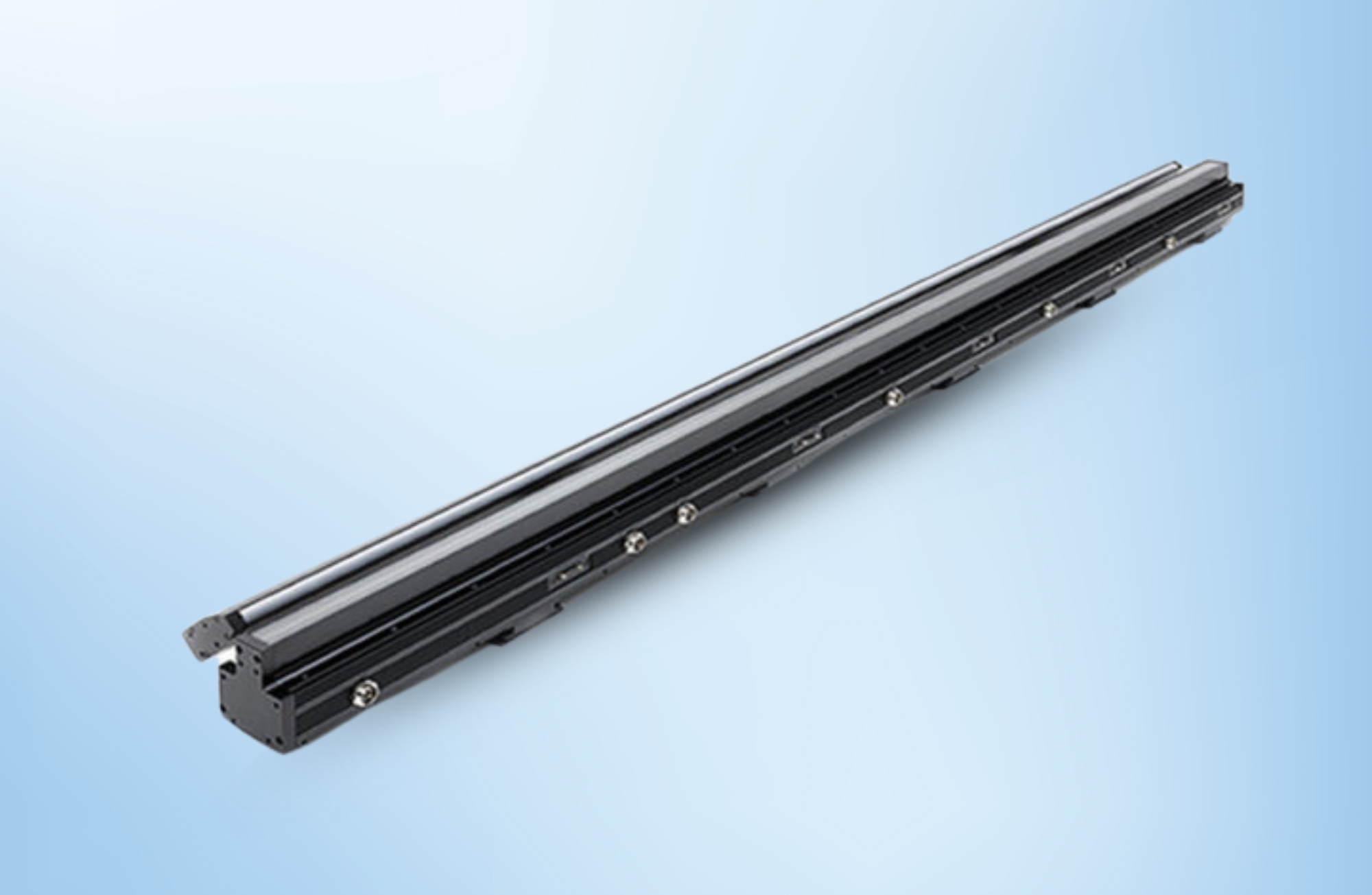

How Does a CIS Camera Work?
CIS cameras use a line-scan technique. Unlike conventional area-scan cameras, which capture a two-dimensional image all at once, CIS cameras scan objects line by line. This is particularly useful in applications where continuous, high-resolution surface inspection is required.
Here’s a breakdown of the CIS camera's components and workflow:
- Light Source: The object to be imaged is illuminated using a built-in LED light source, providing uniform illumination across the scanning surface.
- Optical System: The light reflected off the object passes through an optical system (typically a lens) which focuses the image onto the linear sensor.
- Linear Sensor: The linear sensor, also called a CIS module, contains an array of photodiodes or CMOS/CCD sensors that detect the intensity of light at each point. The sensor captures one line of the image at a time, producing a digital representation of the object.
- Motion: The object is moved (typically on a conveyor or roller system) underneath the camera. As the object moves, the camera continuously captures one line of pixels after another. This stream of data is then assembled into a full high-resolution image.
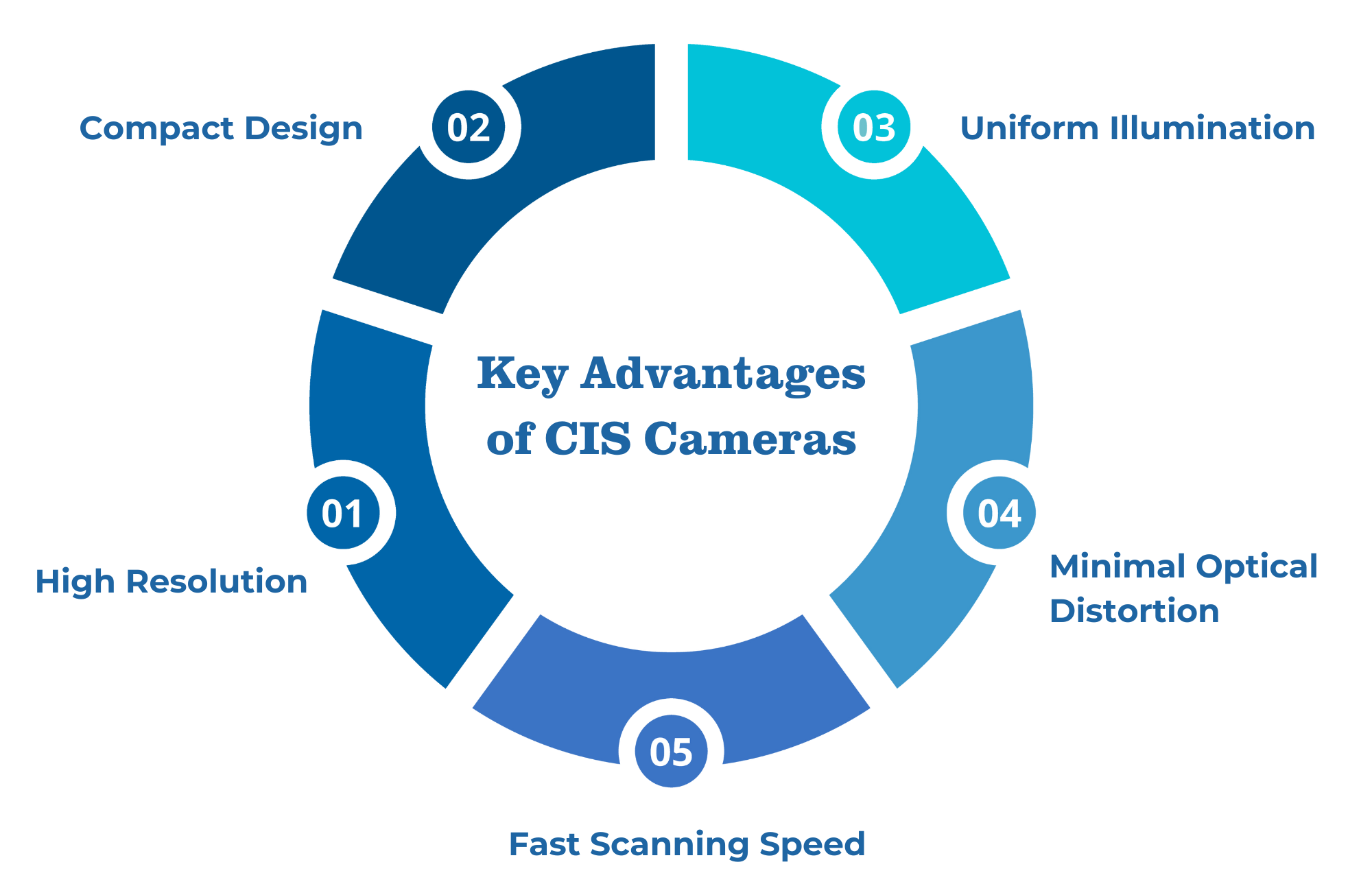
Key Advantages of CIS Cameras
CIS cameras offer a unique set of advantages compared to conventional area-scan cameras, especially in specific industrial and inspection applications.
1. High Resolution
CIS cameras are capable of capturing extremely fine details thanks to their high pixel density. This is crucial in industrial applications, where the detection of microscopic defects on surfaces such as metal, textiles, or glass is essential for quality control.
2. Compact Design
One of the standout features of CIS technology is its compact form factor. The sensor, optics, and lighting are all housed in a single, integrated module. This makes CIS cameras much smaller and lighter than traditional area-scan cameras, allowing for easier installation in tight spaces or compact production lines.
3. Uniform Illumination
With the light source integrated directly into the CIS camera, illumination is highly uniform. This is a significant advantage for surface inspection, where variations in lighting can lead to inconsistent image quality and errors in defect detection.
4. Minimal Optical Distortion
The design of CIS cameras, with their close proximity between the lens and sensor, reduces optical distortion and aberrations. This ensures that images remain sharp and accurate across the entire field of view.
5. Fast Scanning Speed
Because CIS cameras capture images line by line as the object moves past, they can achieve high speeds without sacrificing resolution. This is ideal for high-speed production lines where surface inspection needs to happen in real-time without slowing down the process.
Common Applications of CIS Cameras
CIS cameras are widely used in industries where precise, high-speed surface inspection is required. Some of the common applications include:
Surface Inspection
CIS cameras are used in industries such as printing, packaging, and semiconductor manufacturing to inspect the surfaces of materials like paper, plastics, and metal for defects. For example, they can detect scratches, blemishes, or other surface irregularities that would compromise product quality.
PCB and Electronic Inspection
In electronics manufacturing, CIS cameras are used to inspect printed circuit boards (PCBs) for defects like misaligned components, missing solder, or cracks. The high-resolution line-scan capabilities of CIS cameras make them perfect for capturing the fine details required in PCB inspection.
Textile and Fabric Inspection
For industries involved in textile and fabric production, CIS cameras play a crucial role in identifying defects such as weaving errors, thread inconsistencies, or holes. These cameras can operate at high speeds, making them ideal for continuous inspection on fast-moving textile production lines.
Glass and Metal Sheet Inspection
CIS cameras are often used to inspect flat, reflective surfaces like glass and metal sheets for scratches, dents, and other defects. The cameras can be configured to capture images with minimal reflection and distortion, ensuring an accurate inspection.
Battery Foil Inspection
During the manufacturing of battery foils, CIS cameras are deployed to inspect for defects during coating, slitting, or lamination processes. In industries such as electric vehicle battery production, detecting any imperfections on the foil surface is critical to ensuring product reliability.

Limitations of CIS Cameras
While CIS cameras have many advantages, they are not without limitations:
- Limited Depth of Field: CIS cameras have a very limited depth of field, which makes them unsuitable for inspecting three-dimensional objects or objects with significant variations in height.
- Line-Scan Requirement: CIS cameras need the object to move across the field of view to capture a complete image, which limits their use in applications where the object is stationary or irregularly shaped.
- Limited working distance: CIS imaging systems need shorter working distance. The distance between the camera and object is generally between 15mm to 30 mm. This is ideal for sheet inspection where materials are moving at high speed and maintaining a stable surface.
CIS cameras represent a powerful tool in the realm of industrial imaging, particularly for applications requiring high-speed, high-resolution surface inspection. Their compact design, built-in illumination, and ability to minimize optical distortion make them ideal for industries like printing, electronics, textiles, and manufacturing, where quality control is paramount.
While they may not be suitable for every imaging application due to their limited depth of field and line-scan requirements, CIS cameras continue to be an essential technology for detailed surface inspections and precision defect detection. As industrial automation advances, CIS technology is likely to see even broader adoption in diverse applications across multiple sectors.
Understanding how CIS cameras work and their key advantages will enable you to make informed decisions when selecting imaging systems for industrial applications, ensuring that your quality control processes are both efficient and accurate.

