What are Line Scan Cameras, their Function, Features, and Applications?
Published on: Aug 12, 2024

Written by: Admin
What is a Line Scan Camera?
A line scan camera captures images one line at a time using a linear pixel array, building a complete image as the camera or subject moves, ideal for detailed scanning applications.

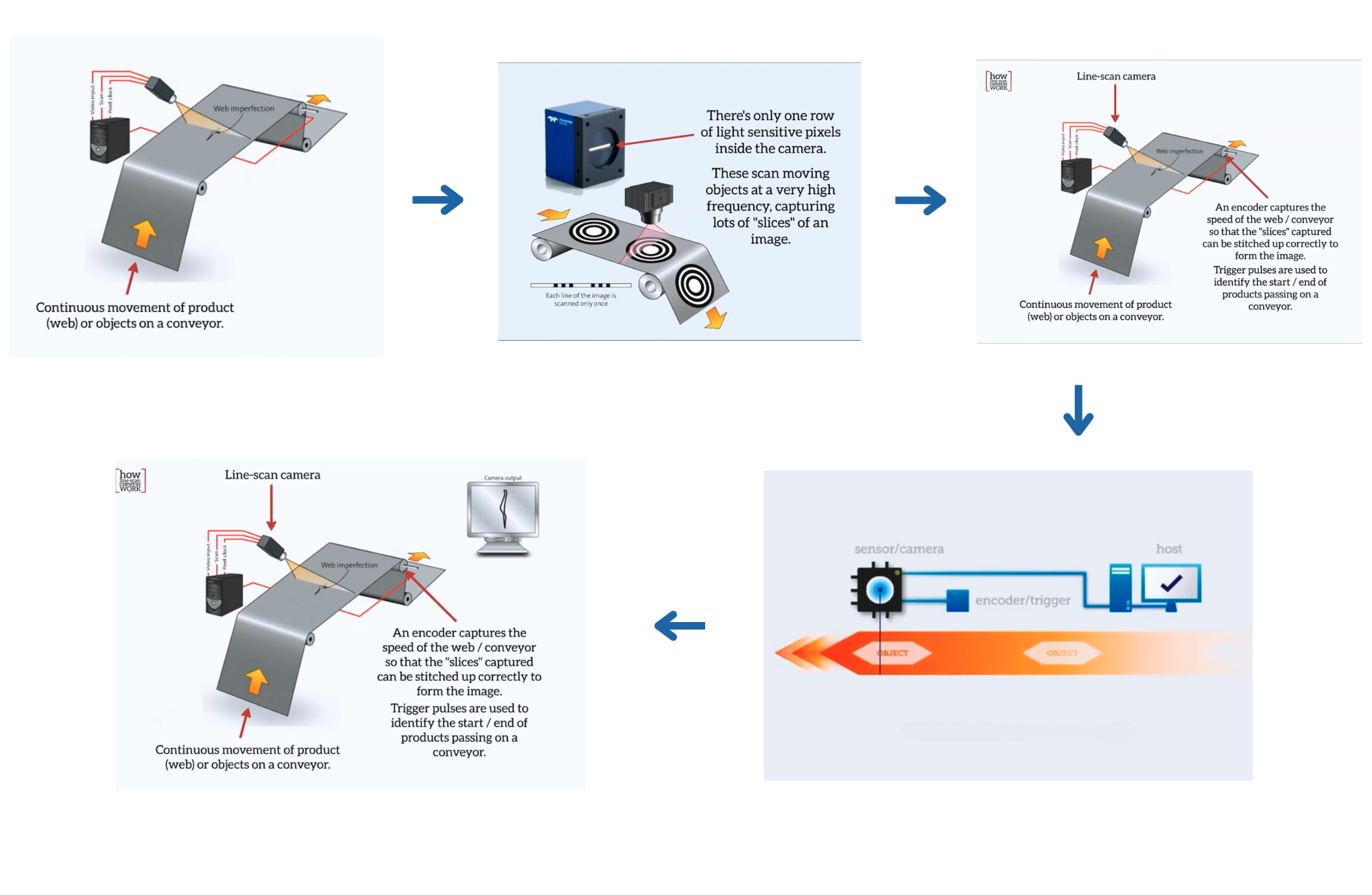
How Line Scan Cameras Work
- Line Sensor:
- The camera contains a single row of photosensitive elements (pixels) arranged in a line. Each pixel captures light intensity for its respective position along the line.
- Scanning Motion:
- The camera or the subject moves in a controlled manner, allowing the line sensor to sequentially capture successive lines of the image. This movement can be continuous or in steps, depending on the application.
- Image Reconstruction:
- As each line is captured, the camera's processing unit stitches these lines together to form a complete image. This method allows for capturing images with very high resolutions along the scanning axis.
Key Features and Advantages
- High Resolution:
- Line scan cameras can achieve extremely high resolutions because the length of the image is not limited by the sensor size. The resolution along the scanning axis depends on the precision and speed of the movement.
- Uniform Illumination:
- Ensures uniform illumination across the entire field of view, reducing lighting inconsistencies.
- High Speed:
- Suitable for high-speed applications as they can capture images quickly without the need for large sensor arrays.
Applications of Line Scan Cameras
-
Line scan cameras are ideal for applications requiring detailed inspection, high resolution, and consistent image quality across large or moving objects. Some common use cases include:
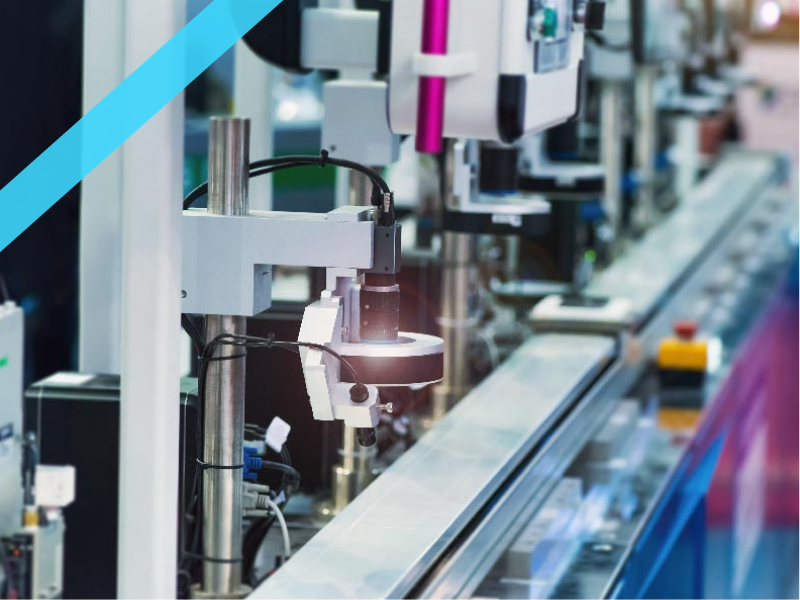
- Industrial Inspection:
- Use Case: Inspecting products on a production line for defects or quality control.
- Advantage: High resolution and speed allow for precise inspection of fast-moving items.
- Print Inspection:
- Use Case: Checking the quality of printed materials such as newspapers, magazines, and labels.
- Advantage: Ability to capture fine details and detect defects over large print surfaces.
- Web Inspection:
- Use Case: Monitoring continuous materials such as paper, textiles, or metal sheets during production.
- Advantage: Continuous scanning capability ensures complete coverage and detection of defects.
- Surface Inspection:
- Use Case: Inspecting surfaces of large objects like aircraft wings, vehicle bodies, or ship hulls.
- Advantage: Ability to scan large, continuous surfaces with high precision.
- Document Scanning:
- Use Case: Digitizing large-format documents, books, or artworks.
- Advantage: High-resolution scanning ensures accurate reproduction of the original material.

When to Use Line Scan Cameras Over Global Shutter Cameras
Line scan cameras are preferred over global shutter cameras in specific scenarios where continuous and high-resolution imaging of moving objects or large surfaces is required. Here are some situations where line scan cameras are advantageous:
- Continuous Web Inspection:
- Use Case: Inspecting continuous materials like paper, textiles, or metal sheets during production.
- Advantage: Line scan cameras can capture high-resolution images of continuous surfaces without gaps or distortions, providing uniform illumination and detailed inspection.
- Large Object Scanning:
- Use Case: Imaging large objects or surfaces, such as aircraft wings, vehicle bodies, or ship hulls.
- Advantage: Line scan cameras can scan large areas with high resolution, ensuring detailed and accurate imaging.
- High-Speed Conveyor Systems:
- Use Case: Inspecting products moving at high speeds on conveyor belts.
- Advantage: Line scan cameras can capture clear and detailed images of fast-moving objects without motion blur, unlike area scan cameras with rolling shutters.
- Print Inspection:
- Use Case: Checking the quality of printed materials like newspapers, magazines, and labels.
- Advantage: Line scan cameras provide high-resolution images of printed materials, ensuring detailed inspection and defect detection.
- Document Scanning:
- Use Case: Digitizing large-format documents, books, or artworks.
- Advantage: Line scan cameras can scan large documents with high resolution and consistency, ensuring accurate reproduction.
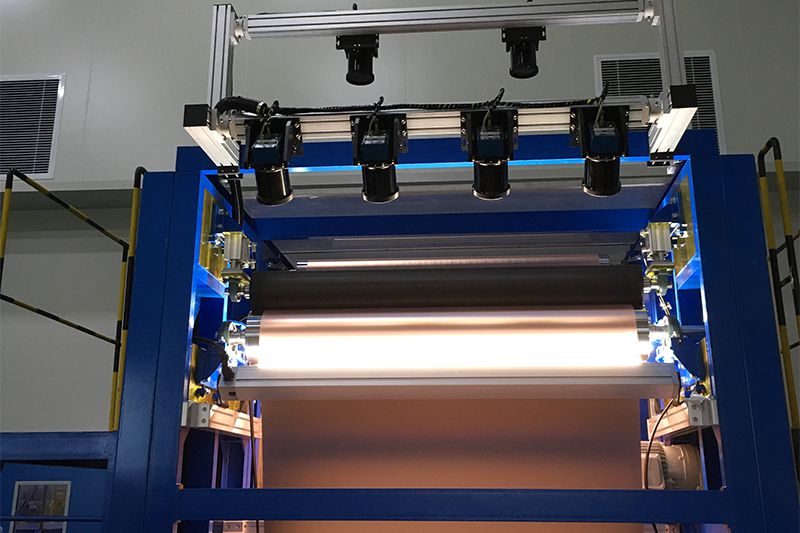

Line scan cameras are powerful tools for applications that require continuous, high-resolution imaging of moving objects or large surfaces. They are ideal for industrial inspection, print and web inspection, large object scanning, high-speed conveyor systems, and document scanning. When choosing between a line scan camera and a global shutter camera, consider the specific requirements of your application, including the need for high-speed motion capture, resolution, and the nature of the objects or surfaces being imaged.

