Creating an Automated Inspection Line: A Comprehensive Guide
Published on: Nov 18, 2024

Written by: Soumen das
Creating an Automated Inspection Line: A Comprehensive Guide
The advent of automation technology has significantly transformed industries, particularly in the area of quality control. Automated inspection lines are becoming integral in manufacturing and production processes, offering the ability to increase efficiency, reduce human error, and improve product quality.
What is an Automated Inspection Line?
An automated inspection line refers to an automation system that uses advanced technologies, such as sensors, cameras, AI and robotic arms, to inspect products or materials as they move along the production line. The goal is to identify defects, measure quality, ensure adherence to specifications, and ensure the final product meets the required standards. Automated inspection systems can perform various tasks, such as visual inspection, dimensional measurement, surface defect detection, and even automated testing of electrical or mechanical properties.
These lines are commonly used in industries like automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, food production, and packaging, where consistency, precision, and speed are essential.
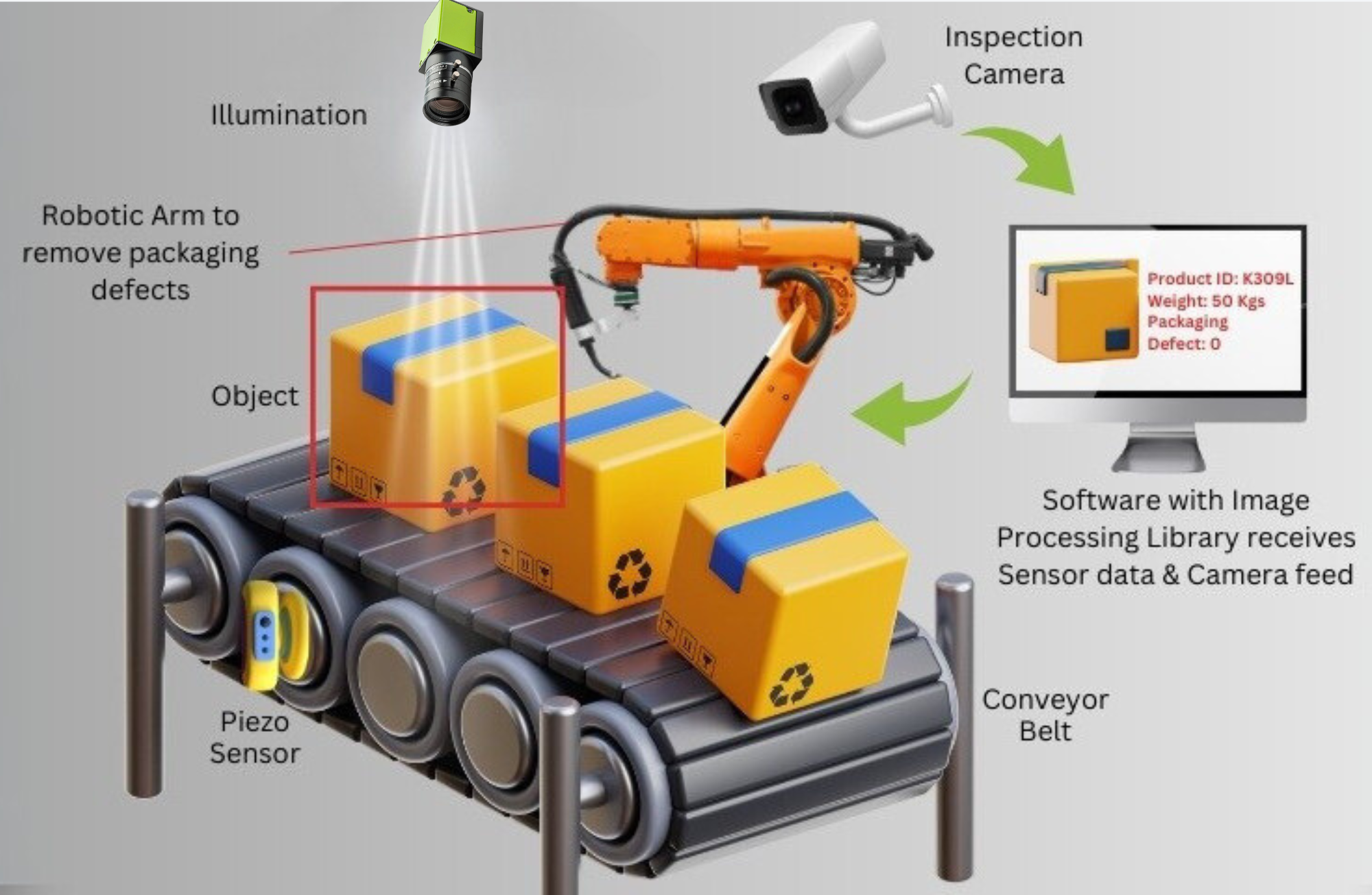
Key Components of an Automated Inspection Line
Creating an efficient automated inspection line requires a combination of hardware, software, and control systems. Below are the essential components of such a system:
Sensors and Cameras: Sensors and cameras are the eyes of the inspection system. Depending on the requirements, different types of cameras may be used:
- Machine Vision Cameras: These cameras capture high-resolution images and send them to image processing systems for analysis.
- Thermal Cameras: Used for temperature-based inspections, such as identifying overheating or heat-related defects.
- Laser Sensors: Employed for precise measurements, such as detecting surface irregularities or measuring dimensions.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These are used for detecting internal defects, such as cracks or voids in materials.
Lighting Systems Proper lighting is critical for automated inspection. Consistent and controlled lighting ensures that images captured by cameras are clear and of high quality. Types of lighting systems include:
- Ring Lights: Provide uniform illumination around the object.
- Backlighting: Used to highlight contours or defects on the surface.
- Diffuse Lights: Reduce shadows and provide soft, even lighting.
Robotic Arms and Conveyors : Automated robotic arms can be integrated into the inspection line to pick up, move, or reorient products for inspection. Conveyor systems help transport products through various stages of inspection without manual intervention. These systems can be equipped with sensors to monitor the speed and position of products.
Software and Image Processing Algorithms : Once images are captured by cameras, they are processed by software to identify defects or deviations. Image processing algorithms analyze the captured data to compare it against a predefined standard or template. These algorithms use techniques such as edge detection, pattern recognition, and pixel analysis to detect anomalies.
Automated Testing Equipment : For certain products, additional testing equipment might be required. For example, an inspection line in the electronics industry may include automated electrical testing stations to verify the functionality of components like circuit boards.
Control Systems and Data Collection : The control system, typically a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) or a PC-based system, coordinates all components of the automated inspection line. The system controls the flow of products, manages inspection data, and triggers actions if a defect is detected. Data collection tools are also integrated to capture performance metrics, defect types, and production information for reporting and analysis.

Steps to Create an Automated Inspection Line
Creating an automated inspection line involves careful planning and design to ensure that it fits the specific needs of the manufacturing process. Below are the steps involved:
Define the Inspection Requirements
The first step in creating an automated inspection line is to clearly define the inspection criteria. This includes identifying:
- The types of defects or quality issues to be detected (e.g., surface defects, dimensional issues, color discrepancies).
- The inspection methods (e.g., visual inspection, dimensional measurement, temperature analysis).
- The required level of accuracy and resolution for detection.
- The speed of the production line and how it will affect inspection time.
These requirements will dictate the types of sensors, cameras, and software you need to implement.
Select Appropriate Inspection Technologies
Based on the defined inspection requirements, you will need to choose the right inspection technologies. For example:
- For visual inspection: Machine vision systems with high-definition cameras and sophisticated image processing software are ideal.
- For dimensional inspection: Laser sensors or 3D vision systems are effective at measuring physical dimensions accurately.
- For thermal analysis: Infrared or thermal cameras can help detect heat-related issues.
Additionally, determine whether the inspection system will operate autonomously or if human intervention will still be required for certain tasks.
Design the Layout of the Automated Line
Once the technologies are selected, the next step is to design the physical layout of the inspection line. This includes:
- Positioning sensors, cameras, and other equipment along the conveyor system.
- Integrating robotic arms or other automated tools for handling products.
- Ensuring that products are positioned correctly for accurate inspection.
- Planning for ease of maintenance and troubleshooting access.
The design should optimize the flow of products through the inspection process to avoid delays and bottlenecks.
Install the Inspection Equipment
After the layout is finalized, the next step is to install the necessary equipment. This involves setting up sensors, cameras, lighting systems, conveyors, and robotic arms. During installation, it’s important to ensure proper calibration of all components to ensure accurate inspection results.
In addition, connect the control systems, which will manage the entire inspection process, including product movement, defect detection, and reporting.
Integrate Software and Data Analysis Tools
With the hardware in place, it’s time to integrate the software systems. The software will manage image processing, data collection, and defect detection. This is also where machine learning algorithms can be applied to improve the system's ability to detect new and evolving defects over time.
The data collected by the system should be fed into a central database or analytics platform, where it can be reviewed in real time or analyzed for trends over time.
Test the System
Before fully deploying the automated inspection line, comprehensive testing should be performed to verify that everything is functioning as intended. This includes:
- Verifying that the sensors and cameras can detect defects accurately and reliably.
- Ensuring that the conveyor and robotic arms are moving products without delays or jams.
- Checking the software’s defect detection capabilities and data reporting features.
Testing should be done with various sample products to ensure that the system works under different conditions and that it meets the specified accuracy requirements.
Deploy and Monitor the System
After successful testing, the automated inspection line can be deployed for full-scale operation. During the initial phase of operation, it’s essential to monitor the system closely to ensure everything is working smoothly. Continuous monitoring helps to catch any minor issues before they escalate, ensuring that the inspection line operates at optimal efficiency.
Additionally, regular maintenance and software updates should be scheduled to keep the system running smoothly and address any potential issues.
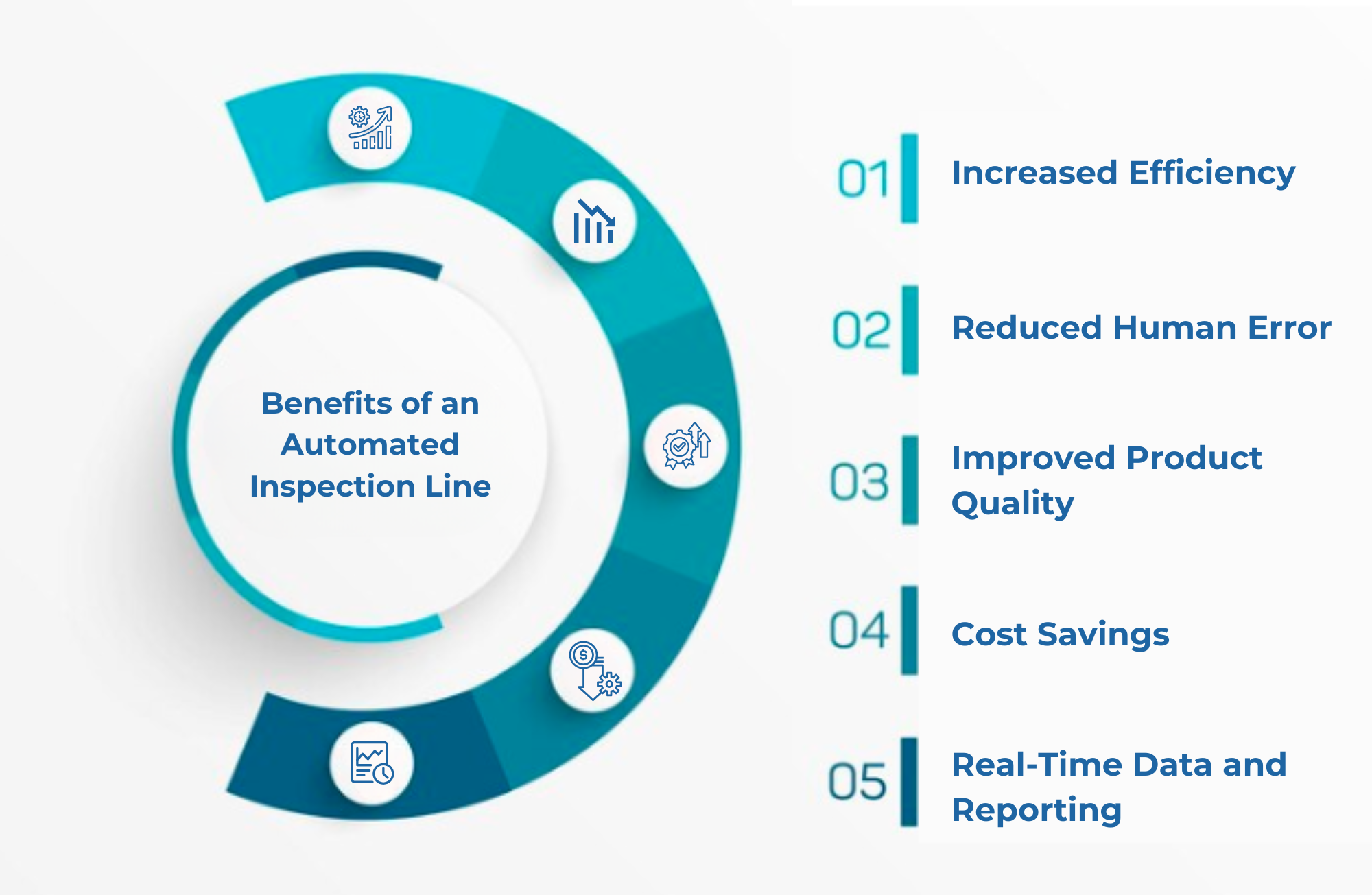
Benefits of an Automated Inspection Line
- Increased Efficiency Automated inspection lines significantly increase the speed and throughput of manufacturing processes, enabling products to be inspected faster than manual inspection methods while maintaining high accuracy.
- Reduced Human Error Automation eliminates the risk of human error, ensuring that defects are consistently identified, and product quality remains high.
- Improved Product Quality Automated systems can detect minute defects that may be overlooked by the human eye, ensuring that only products that meet quality standards move to the next stage of production.
- Cost Savings While the initial investment can be high, over time, automated inspection lines lead to cost savings by reducing labor costs, minimizing scrap and rework, and preventing costly product recalls.
- Real-Time Data and Reporting Automated systems provide real-time feedback and detailed reports, allowing for proactive quality control and quick identification of recurring issues or trends.
Challenges in Implementing an Automated Inspection Line
- High Initial Investment One of the most significant challenges in implementing an automated inspection line is the upfront cost, which includes the purchase of equipment, software, and installation services.
- Integration with Existing Systems Integrating the automated inspection line with existing manufacturing equipment and workflows can be complex, requiring careful planning and customization.
- Maintenance and Calibration Automated systems require regular maintenance and calibration to ensure they continue functioning accurately. This can incur additional costs and downtime.
- Limited Flexibility Some automated inspection systems are highly specialized and may not easily adapt to changes in production or new defect detection requirements.
Creating an automated inspection line is a powerful way to enhance quality control, improve efficiency, and reduce costs in manufacturing. By carefully selecting the right technologies, designing an optimized layout, and integrating the appropriate software, businesses can implement inspection systems that meet their specific needs. While the initial investment and setup can be challenging, the long-term benefits of automation, including increased accuracy, reduced human error, and improved product quality, make it a worthwhile endeavor for many industries. With the right planning, an automated inspection line can be a game-changer in the production process, ensuring higher standards of manufacturing excellence.

