What is Working Distance in Cameras & Imaging?
Published on: Aug 12, 2024

Written by: Admin
What is Working Distance?
Working distance is the distance between a camera lens and the object being imaged, crucial in applications like microscopy, machine vision, and industrial inspection for precise imaging control.
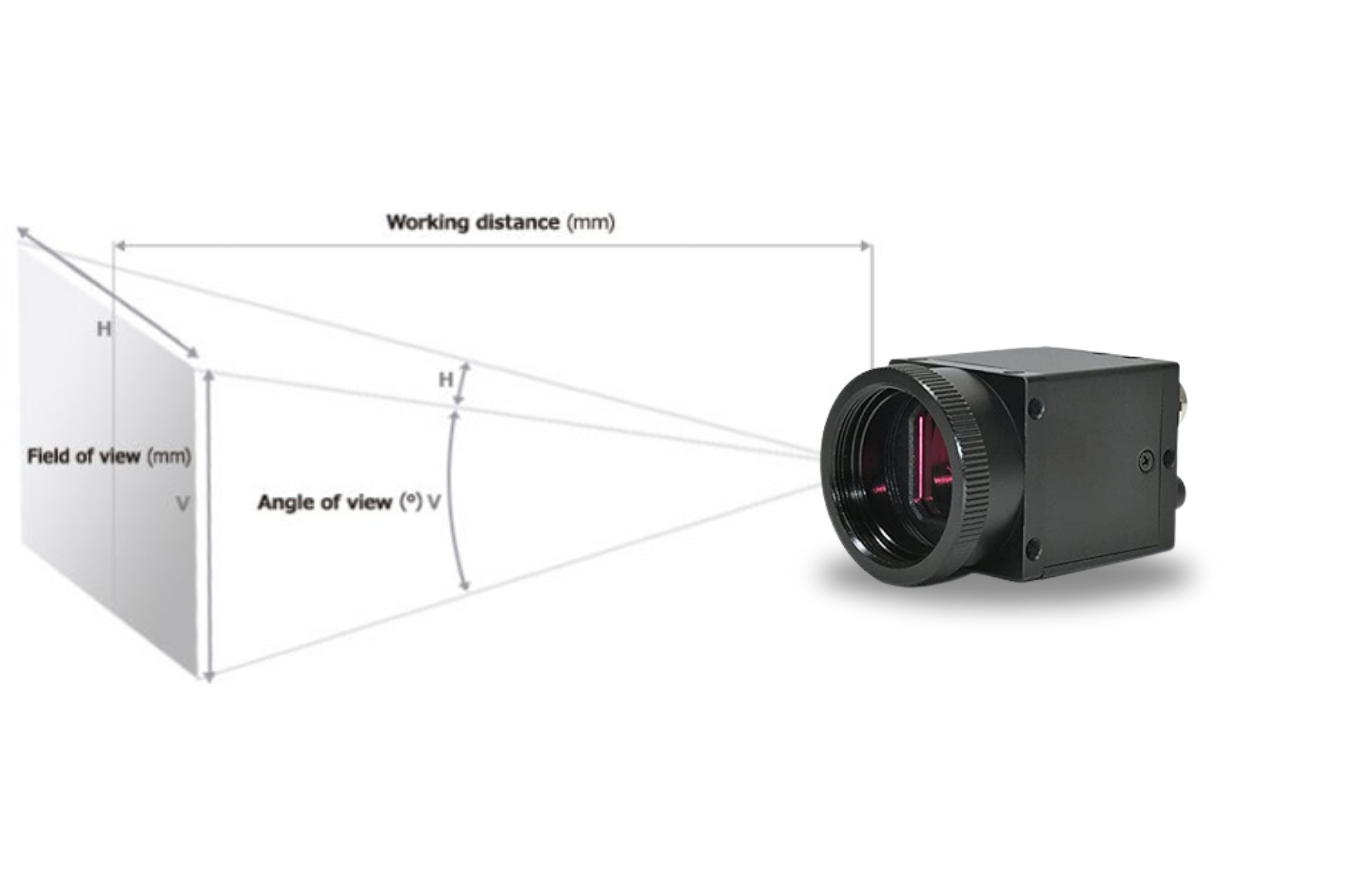
Key Aspects of Working Distance
- Optical Performance: The working distance affects the optical performance of the lens, including magnification, depth of field, and perspective.
- Safety and Accessibility: In industrial and laboratory settings, maintaining an appropriate working distance ensures that the imaging equipment is safe from damage and that the objects are easily accessible for inspection or manipulation.
- Lighting: Adequate working distance allows for proper illumination of the object, which is essential for high-quality imaging.
Relationship Between Field of View (FOV) and Working Distance
Field of View (FOV) is the extent of the observable area that a camera can capture. The relationship between FOV and working distance is an important aspect of imaging system design.
Key Concepts
- FOV Definition: FOV is typically measured in degrees (angular FOV) or in physical dimensions (linear FOV) such as millimeters or inches.
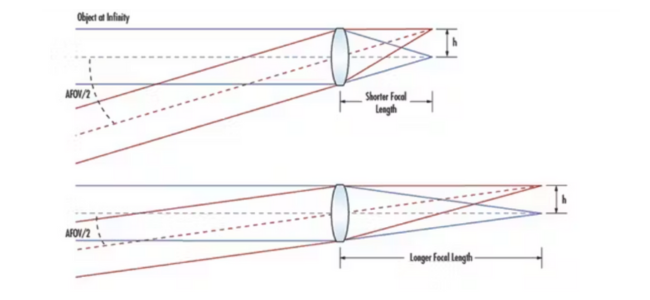
- Inverse Relationship: There is generally an inverse relationship between FOV and working distance for a given lens. As the working distance increases, the FOV also increases, but the magnification decreases.
- Lens Focal Length: The focal length of the lens plays a crucial role in determining the FOV at a given working distance. A lens with a shorter focal length provides a wider FOV, while a lens with a longer focal length provides a narrower FOV.
Mathematical Relationship
For a simple lens system, the linear FOV (FOV_l) can be calculated using the following formula:
FOVl=2×(WD×tan(θ/2))\text{FOV}_l = 2 \times (\text{WD} \times \tan(\theta/2))FOVl=2×(WD×tan(θ/2))
where:
- FOVl\text{FOV}_lFOVl = Linear Field of View
- WD\text{WD}WD = Working Distance
- θ\thetaθ = Angular Field of View
In cases where the angular FOV is small, the tangent function can be approximated, simplifying the formula to:
FOVl≈WD×θ\text{FOV}_l \approx \text{WD} \times \thetaFOVl≈WD×θ
Practical Applications
1. Machine Vision
In machine vision systems used for quality control and inspection, maintaining the correct working distance ensures that the entire object or area of interest is within the FOV. Adjusting the working distance can help in capturing detailed images required for precise measurements and defect detection.
2. Microscopy
In microscopy, working distance is crucial for maintaining focus and avoiding contact with the specimen. Long working distance objectives allow for more space between the lens and the specimen, which is essential for observing live specimens or working with additional equipment like manipulators.
3. Industrial Inspection
For industrial inspection systems, the working distance must be set to accommodate the size of the objects and the required resolution. A balance between working distance and FOV is necessary to ensure that the imaging system captures all relevant details without compromising image quality.
4. Photography and Videography
In photography, particularly macro photography, working distance influences the composition and lighting of the subject. A shorter working distance allows for greater magnification and detail but may require careful lighting arrangements to avoid shadows and reflections.
Working distance is a fundamental parameter in camera and imaging systems, affecting optical performance, safety, accessibility, and lighting. Understanding the relationship between FOV and working distance helps in designing and optimizing imaging systems for various applications, from machine vision and microscopy to industrial inspection and photography. By carefully adjusting the working distance and choosing the appropriate lens, one can achieve the desired balance between FOV and magnification, ensuring high-quality and effective imaging results.

