Machine Vision System
Published Jun 12, 2024
Imagine a factory where machines can not only produce products but also "see" and understand what's happening around them - what are they producing, How many are they producing, are there any defects within those products?. This is the power of machine vision, a technology revolutionizing manufacturing by giving machines the ability to analyze the physical world.
What is a Machine Vision System?
machine vision system is a powerful combination of hardware and software. Here's the breakdown:
- Hardware: High-resolution cameras capture visual data, acting as the eyes of the system.
- Software: The brains behind the operation. Sophisticated algorithms powered by AI and machine learning analyze the captured images. These algorithms are trained on vast amounts of data, allowing them to identify objects, classify them, and even detect anomalies.
Machine Vision in Action: A Manufacturing Advantage
Machine vision offers a range of benefits for manufacturers, boosting efficiency, quality, and overall productivity:
- Enhanced Quality Control: Machine vision excels at inspecting products with superhuman precision. It can detect even the subtlest defects that human inspectors might miss, ensuring only flawless products reach the market.
- Reduced Waste: minimizing defects, machine vision leads to significant cost savings. Less wasted materials and fewer rejected products translate to a healthier bottom line.
Beyond Inspection: A Multifaceted Tool
Machine vision isn't limited to just inspection. It provides a comprehensive set of tools for various stages of manufacturing:
- Counting with Confidence: Need to keep track of inventory? Machine vision can accurately count objects, whether finished products rolling off the line or individual components within an assembly. This ensures accurate stock control and prevents delays.
- Product Identification: Machine vision can identify specific products using techniques like barcode reading or optical character recognition (OCR). This allows for tracking products through production and ensures correct packaging and labeling.
- Flawless Packaging: Properly sealed and undamaged packaging is crucial. Machine vision can identify missing seals, tears, or dents, guaranteeing product integrity before shipment.
- Robotic Guidance: Imagine robots equipped with machine vision! They can navigate production lines with precision, perform assembly tasks accurately, and efficiently pick and place objects.
The Future of Manufacturing: A Clear Visionl
The potential of machine vision in manufacturing keeps expanding. As it integrates with AI, the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics, factories will become even smarter and more interconnected. This will lead to:
- Predictive Maintenance: Machine vision can identify equipment issues before they cause breakdowns, preventing costly downtime
- Self-Optimizing Production Lines: Real-time data from machine vision systems can be used to automatically adjust production parameters for optimal efficiency.
How Machine Vision Systems Work
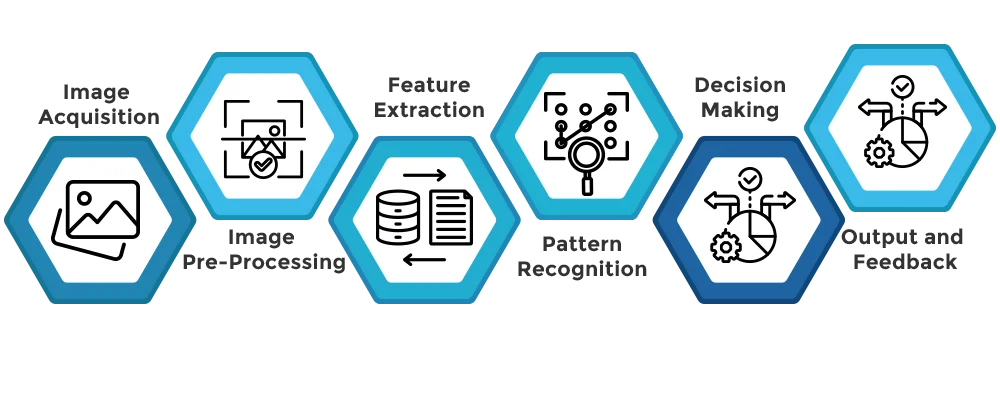
The operation of a machine vision system involves several sequential steps:
- Image Acquisition:
The system captures an image or a series of images using the cameras. The quality of these images is fundamental to the success of the subsequent processing steps.
- Image Pre-Processing:
The captured images may undergo pre-processing to enhance their quality. This could include filtering, scaling, adjusting contrast, or correcting brightness to highlight key features.
- Feature Extraction:
In this step, specific features of interest within the image are identified and extracted. These could be edges, shapes, textures, or colors that are relevant to the inspection task.
- Pattern Recognition:
The system compares the extracted features against predefined patterns or models to recognize and classify the objects within the image.
- Decision Making:
Based on the recognition results, the system makes decisions or triggers actions. For example, it might reject a defective product, guide a robotic arm, or alert an operator to an issue.
- Output and Feedback:
The results of the analysis are outputted to the user or integrated into other systems. Feedback loops can be established to continuously refine and improve the process based on the outcomes.
In conclusion, machine vision is not just a technology; it's a transformative force in manufacturing. By providing machines with the ability to "see," it empowers manufacturers to achieve unparalleled levels of quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. As this technology continues to evolve, the future of manufacturing looks remarkably clear, with machine vision leading the way.

