What factors should be considered while choosing machine vision camera for inspection automation in manufacturing
Published on: Jan 27, 2025

Written by: Soumen das
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Machine Vision Camera for Inspection Automation in Manufacturing
Machine vision cameras are essential for modern inspection automation systems, enabling manufacturers to detect defects, ensure quality, and enhance production efficiency. Selecting the right camera for a specific inspection application involves understanding various factors that influence the system's accuracy, reliability, and performance.
Defect Size
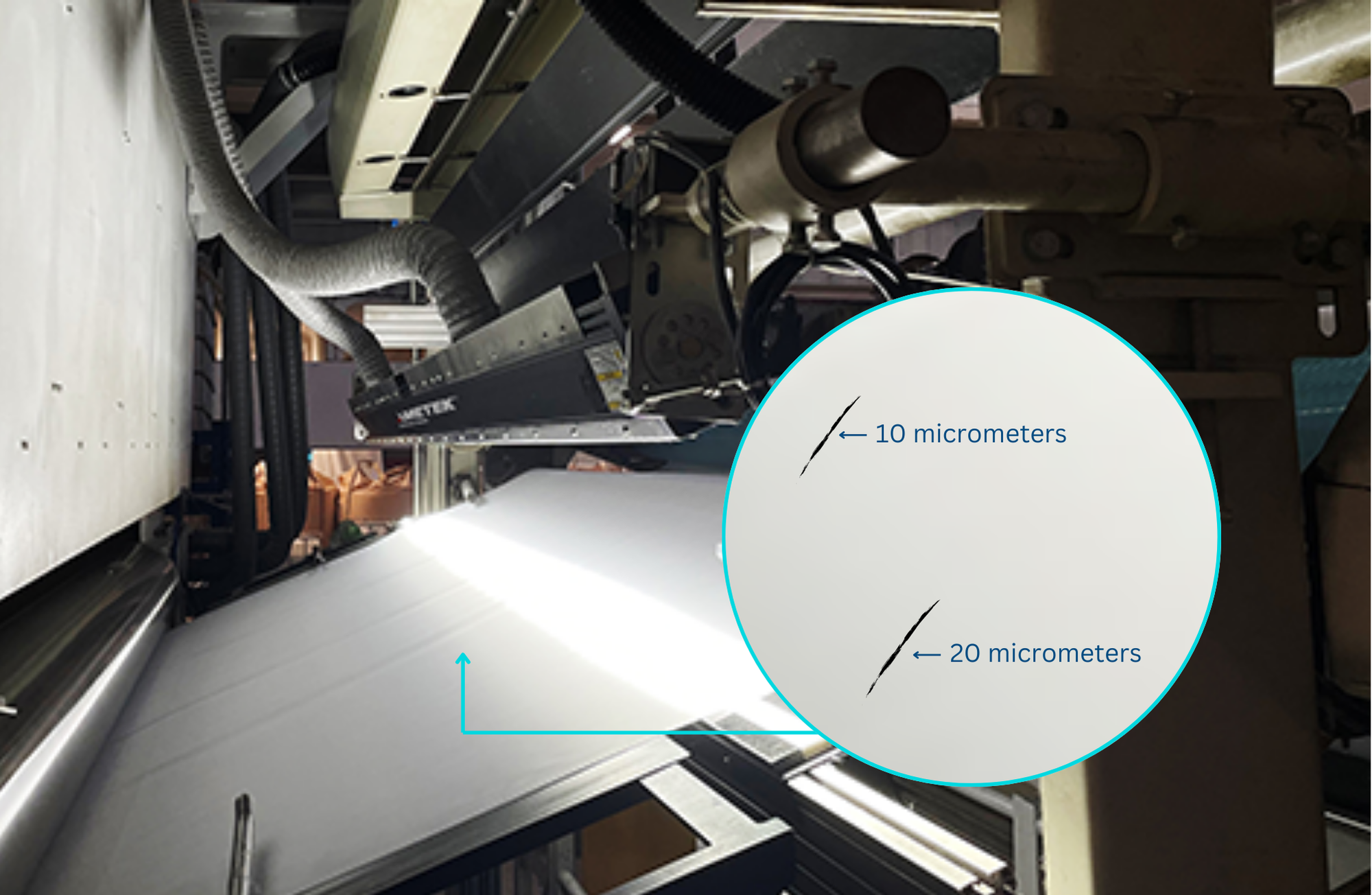
Defect size is the most crucial factor in selecting a machine vision camera. The camera must be capable of capturing the smallest defects with sufficient clarity for accurate detection.
- Micron-Level Defects:
- For defects as small as a few microns, a camera with a high-resolution image sensor is essential to ensure that the defect occupies enough pixels for analysis.
- Example: Detecting pinholes or scratches in metal or plastic surfaces that are 10 to 50 micrometers in diameter.
Key Consideration: Choose a sensor resolution that ensures defects appear in at least 4–5 pixels for effective detection.
Inspection Process: Online or Stationary
The nature of the inspection process—whether the product is stationary or moving—determines the type of camera needed:
- Online Inspection (Moving Products):
- Products such as metal sheets, leather, textiles, aluminum sheets, or films move continuously on a conveyor.
- Line-Scan Cameras:
- Capture images line by line and stitch them together for a continuous view.
- Suitable for inspecting long, wide, or continuously moving materials.
- Stationary Inspection (Static Products):
- Products remain still during inspection.
- Area-Scan Cameras:
- Capture a full image of the product in a single frame.
- Ideal for inspecting smaller, stationary objects like components or assemblies.
Key Consideration: Match the camera type (line-scan or area-scan) to the movement of the product during inspection.

Product Size
The size of the product directly influences the Field of View (FOV) required for inspection.
- Long Products (e.g., Metal Sheets):
- Focus on the width of the product as the FOV for line-scan cameras.
- Small or Standard-Sized Products:
- The FOV must cover the entire surface of the product in one frame for area-scan cameras.
Key Consideration: Ensure the FOV matches the dimensions of the product to avoid missing any part of the surface.
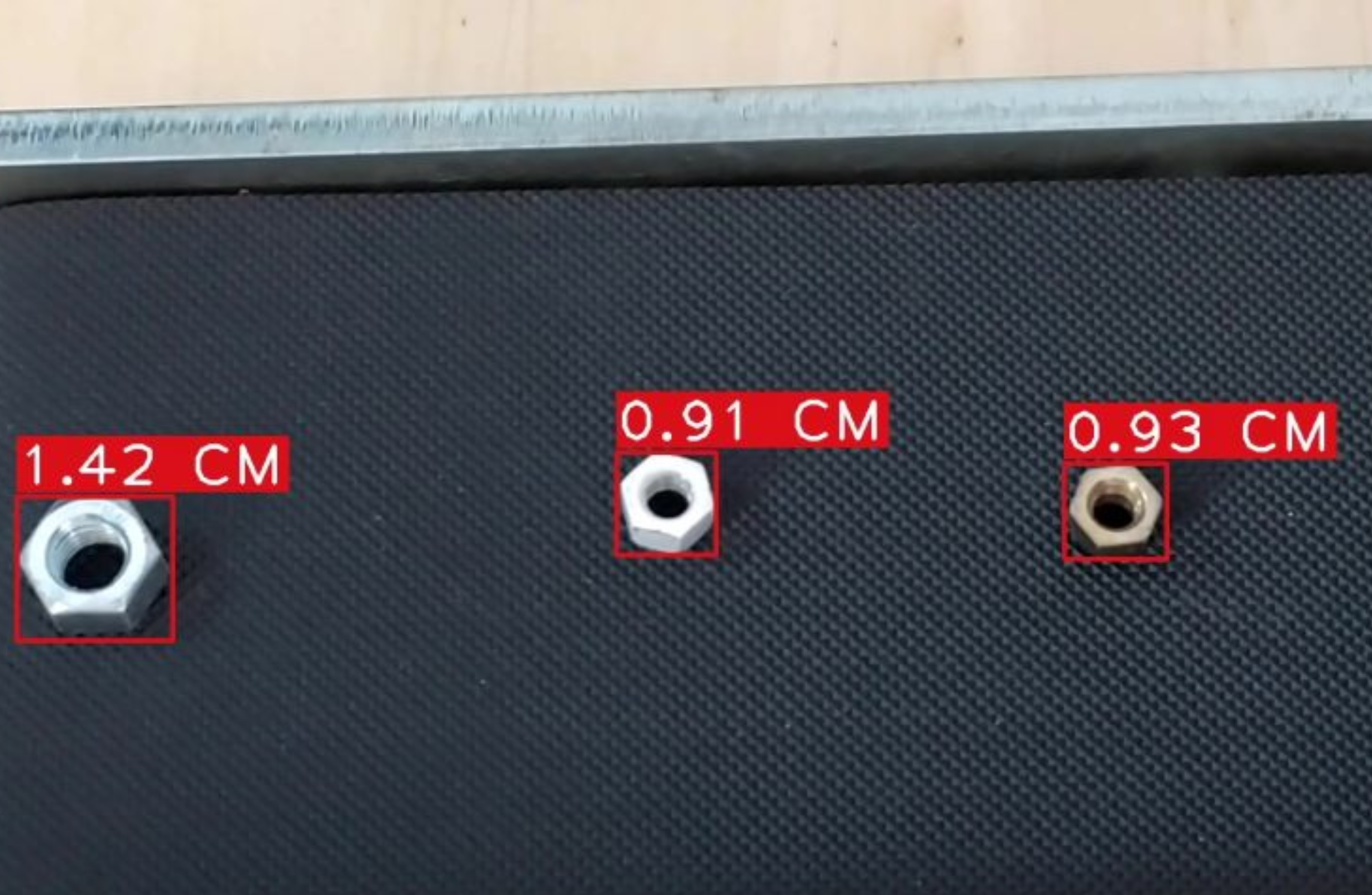

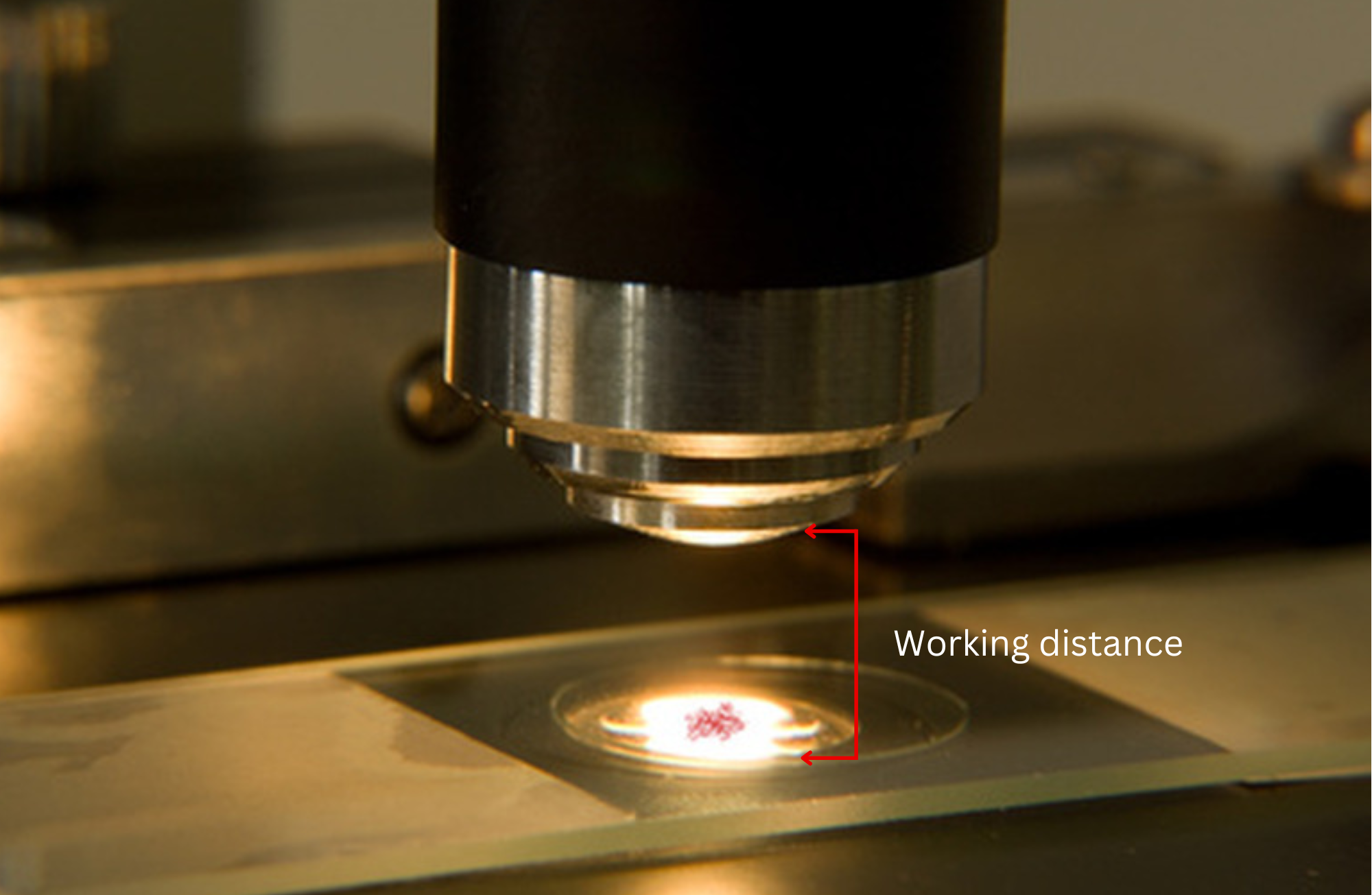
Working Distance
The working distance—the space between the camera and the object—affects lens selection and image quality.
- Long Working Distance:
- Requires lenses with appropriate focal lengths to maintain image clarity.
- Short Working Distance:
- May require special mounting or compact lenses.
Key Consideration: Measure the distance precisely and choose a lens compatible with both the camera and the working distance.
Selecting the Lens
The lens is as critical as the camera itself, influencing image quality and defect detection accuracy. Key factors to consider include:
a. Image Format
- The lens’s image format should be equal to or greater than the camera’s sensor size or target surface.
- Example: If the camera’s image format is 1.1”, the image format of lens must be 1.1” or more.
b. Mounting Type
- Ensure compatibility between the lens and camera mount type (e.g., C-mount, F-mount).
c. Resolution
- The lens resolution should match the camera’s resolution to avoid loss of image detail.
Key Consideration: Select a lens that matches the camera’s specifications and inspection requirements.

Color vs. Monochrome Cameras
- Color Cameras:
- Capture full-color images, making them ideal for applications requiring color differentiation or defect detection based on color variations.
- Monochrome Cameras:
- Capture black-and-white images with higher contrast and finer detail, suitable for texture, edge detection, and surface inspections.
Key Consideration: Use color cameras for color-critical inspections and monochrome cameras for high-contrast or texture-focused tasks.

Lighting Compatibility
Lighting is essential for enhancing defect visibility, and the camera must be compatible with the chosen lighting setup:
- Dark Surfaces:
- Use high-intensity lighting at appropriate angles to reduce glare.
- Light Surfaces:
- Use diffuse lighting to prevent hotspots and shadows.
- Shiny Surfaces:
- Polarized or dark-field lighting can minimize reflections and highlight defects.
Key Consideration: Align camera selection with the lighting strategy for the inspection environment.

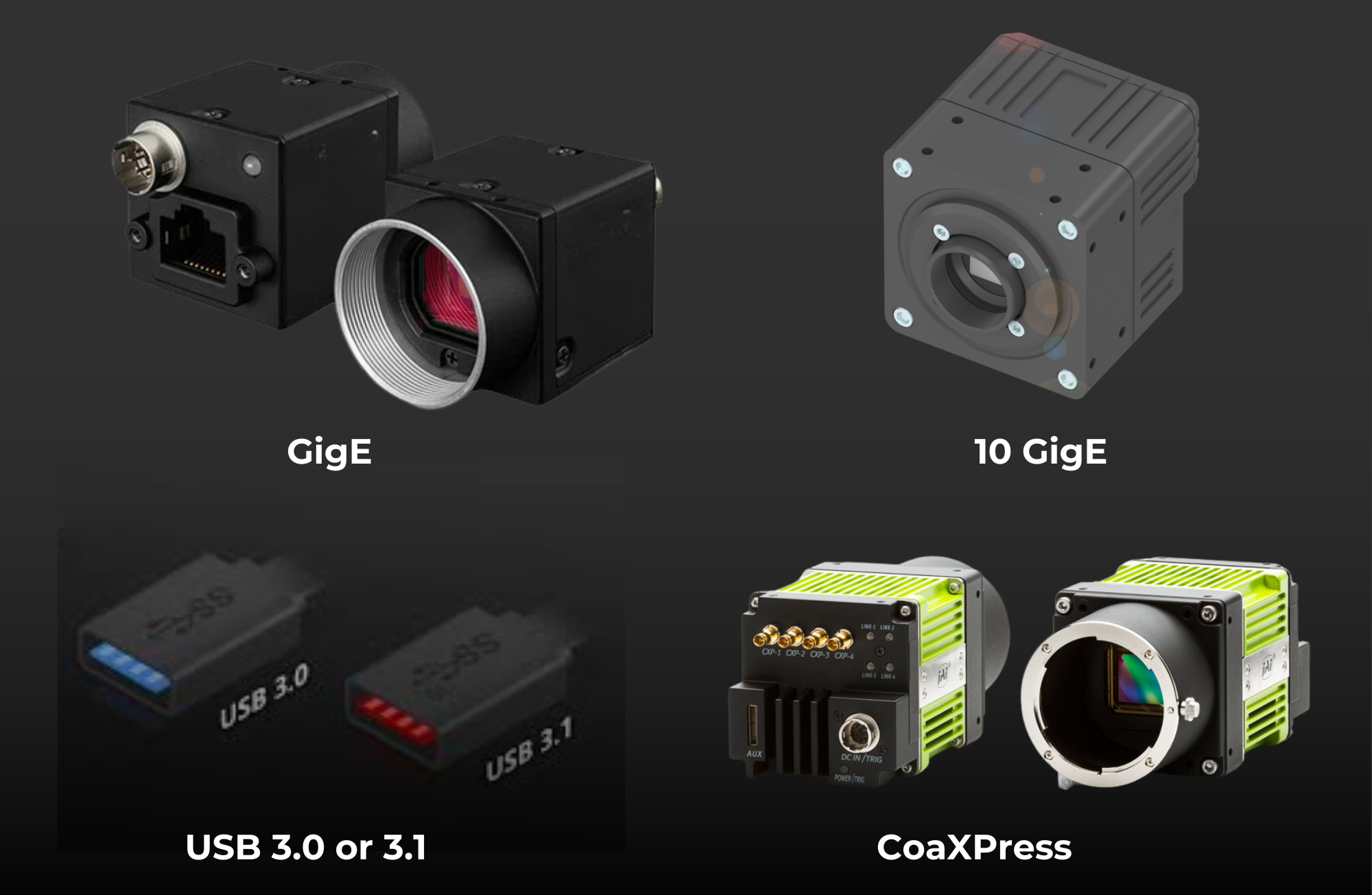
Interface
Machine vision cameras support various interfaces for data transmission to controllers or processing systems:
- GigE (Gigabit Ethernet):
- Common for most applications, offering reliable performance over moderate distances.
- 10 GigE:
- Necessary for high-resolution cameras (e.g., 16K resolution or higher) to handle large data volumes.
- USB 3.0 or 3.1:
- Suitable for shorter distances and less data-intensive applications.
- CoaXPress:
- Ideal for applications requiring ultra-fast data transfer over long distances.
Key Consideration: Choose an interface that matches the camera’s resolution and the distance between the camera and controller.

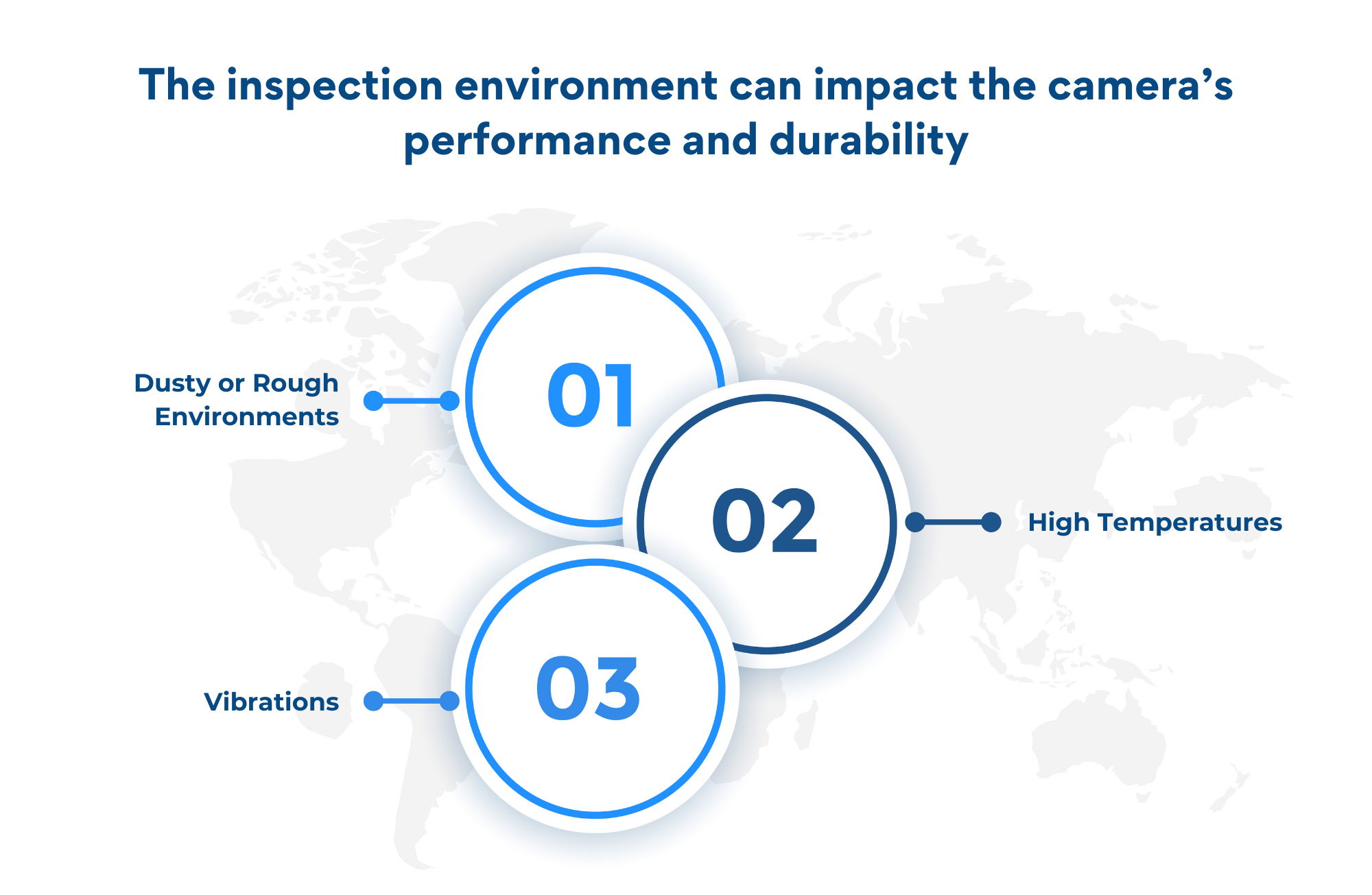
Environmental Factors
The inspection environment can impact the camera’s performance and durability:
- Dusty or Rough Environments:
- Use cameras with protective housings and cooling systems.
- High Temperatures:
- Cameras with built-in cooling or heat-resistant enclosures may be required.
- Vibrations:
- Ruggedized cameras designed to withstand industrial vibrations.
Key Consideration: Ensure the camera is built to withstand the specific environmental conditions of your production line.
Choosing the right machine vision camera for inspection automation in manufacturing requires careful consideration of factors such as defect size, product movement, working distance, lighting, and environmental conditions. By understanding these factors and aligning them with your specific inspection requirements, you can select a camera that ensures optimal performance, accuracy, and efficiency.
Intelgic’s expertise in machine vision systems ensures that manufacturers receive tailored recommendations and solutions for their inspection automation needs. Contact Intelgic today to learn how we can help you implement the perfect vision system for your production line.

