What are CMOS Image Sensors?
Published on: Aug 09, 2024

Written by: Admin
What is a CMOS Image Sensor?
A CMOS image sensor captures images by converting light into electrical signals, known for low power use, high noise immunity, and integration in devices like cameras, smartphones, and industrial systems.
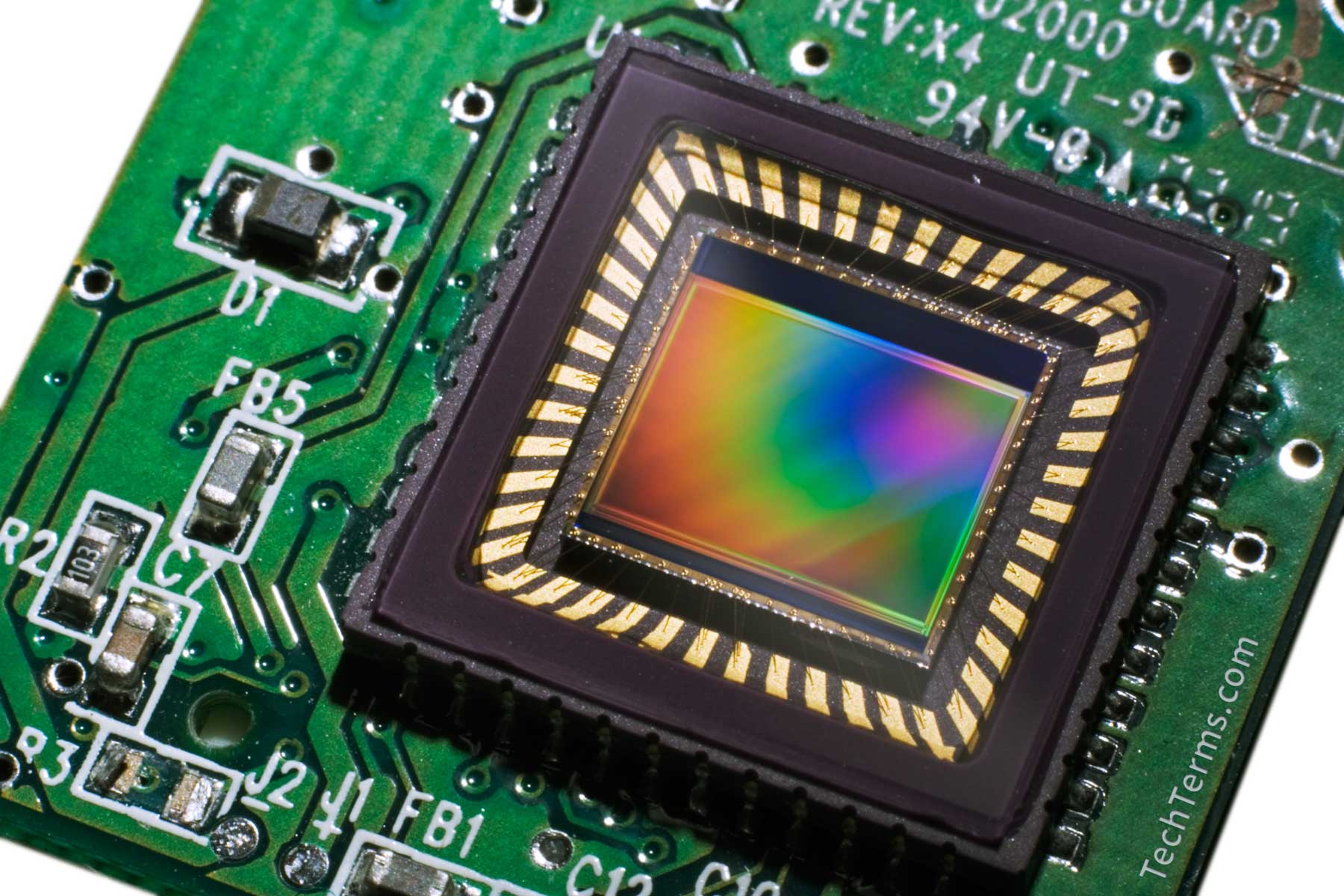
Key Characteristics of CMOS Image Sensors
- High Speed: CMOS sensors can read out images quickly, enabling high frame rates for video capture.
- Low Power Consumption: They consume less power compared to CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) sensors, making them ideal for battery-powered devices.
- Integration: CMOS technology allows the integration of additional circuitry (such as signal processing and ADCs) on the same chip, reducing system complexity and cost.
- Noise Reduction: CMOS sensors typically have lower noise levels, improving image quality.
How Do CMOS Image Sensors Work?
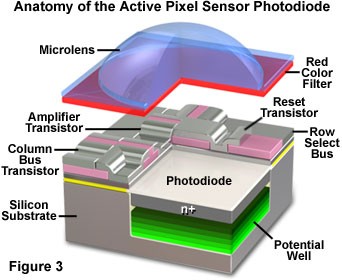
A CMOS image sensor consists of an array of pixel sensors, each of which measures the intensity of light at a specific location. Here's a step-by-step overview of how they work:
1. Photodetection
- Photodiodes: Each pixel contains a photodiode that converts incoming light (photons) into an electrical charge (electrons). The amount of charge generated is proportional to the intensity of the light.
2. Charge Accumulation
- Integration Time: During the exposure period, the photodiodes accumulate charge. The integration time determines how long the photodiodes collect light, affecting the brightness of the image.
3. Charge-to-Voltage Conversion
- Pixel Circuitry: Each pixel has associated circuitry that converts the accumulated charge into a voltage. This typically includes a capacitor and a transistor to amplify the signal.
4. Analog-to-Digital Conversion
- ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter): The analog voltage signal from each pixel is converted into a digital value by an ADC. In CMOS sensors, ADCs can be integrated on the same chip, allowing parallel conversion of multiple pixel signals.
5. Image Readout
- Row-by-Row Scanning: The digital values from the pixels are read out row by row and sent to the image processor, where they are assembled into a complete image.
Advantages of CMOS Image Sensors
1. Low Power Consumption
- Efficiency: CMOS sensors consume less power compared to CCD sensors, making them suitable for portable devices like smartphones and cameras.
2. High Speed and Frame Rates
- Fast Readout: The architecture of CMOS sensors allows for faster readout speeds, enabling high frame rates necessary for video recording and high-speed photography.
3. On-Chip Integration
- Compact Design: CMOS technology allows for the integration of additional functions, such as signal processing and analog-to-digital conversion, on the same chip. This reduces the overall size and cost of the imaging system.
4. Low Manufacturing Cost
- Standard Processes: CMOS sensors can be manufactured using standard semiconductor fabrication processes, which are more cost-effective compared to the specialized processes required for CCD sensors.
5. Better Noise Performance
- Reduced Noise: Advanced designs and technologies in CMOS sensors help reduce noise, leading to improved image quality.
Disadvantages of CMOS Image Sensors
1. Rolling Shutter Effect
- Distortion: Many CMOS sensors use a rolling shutter, which can cause image distortion when capturing fast-moving objects. This occurs because different rows of the sensor are exposed at slightly different times.
2. Lower Sensitivity
- Light Sensitivity: Historically, CMOS sensors had lower sensitivity to light compared to CCD sensors. However, advancements in technology have significantly reduced this gap.
3. Fixed Pattern Noise
- FPN: CMOS sensors can exhibit fixed pattern noise, which appears as a consistent pattern of noise in the image. Modern sensors incorporate various techniques to minimize this effect.
Applications of CMOS Image Sensors
1. Consumer Electronics
- Digital Cameras: Used in a wide range of digital cameras, from DSLRs to compact cameras.
- Smartphones: Found in almost all smartphones, enabling high-quality photography and video recording.
- Webcams: Used in webcams for computers and laptops, providing video capture for conferencing and streaming.
2. Industrial and Scientific Imaging
- Machine Vision: Used in industrial inspection systems for quality control and automation.
- Medical Imaging: Utilized in medical devices such as endoscopes and diagnostic imaging equipment.
- Scientific Research: Employed in telescopes, microscopes, and other scientific instruments for capturing detailed images.
3. Automotive and Security
- Driver Assistance Systems: Used in automotive applications for driver assistance and autonomous driving.
- Surveillance Cameras: Deployed in security and surveillance systems for monitoring and recording.
CMOS image sensors are a critical component in modern imaging devices, offering numerous advantages such as low power consumption, high speed, on-chip integration, and cost-effectiveness. While they have some limitations, advancements in technology have made CMOS sensors highly competitive with other imaging technologies like CCDs. Their widespread use in consumer electronics, industrial applications, and scientific research underscores their importance and versatility in capturing high-quality images. Understanding the principles and benefits of CMOS image sensors is essential for anyone involved in the fields of electronics, imaging, and digital photography.

